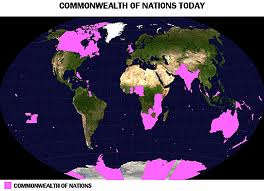
Formerly known as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, The Commonwealth of Nations is an intergovernmental organization which developed from the former members of the British Empire. With the present 54 member states, only Rwanda and Mozambique were not members of the Empire. The framework as outlined in the Singapore Declaration guides the operation of this organization.
The current members of the Commonwealth include Antigua and Barbuda, Australia, Bahamas, Bangladesh, Barbados, Belize, Botswana, Brunei, Cameroon, Canada, Cyprus, Dominica The Gambia, Ghana, Grenada, Guyana, India , Jamaica, Kenya, Kiribati, Lesotho, Malawi, Malaysia, Maldives, Malta, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Nauru, New Zealand, Nigeria, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, Rwanda, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Samoa, Seychelles, Sierra Lone, Singapore, Solomo Islands, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Swaziland, Tanzania, Tonga, Trinidad and Tobago, Tuvalu, Uganda, United Kingdom, Vanuatu, and Zambia. In its history, there were four member countries which were dissolved consisting of Malaya and Newfoundland; two withdrawn members including Ireland and Zimbabwe; and one suspended member which is Fiji.
At present, there are six countries applying for membership namely Algeria, Madagascar, Somaliland, South Sudan, Sudan, and Yemen. Queen Elizabeth II is the symbolic Head of the Commonwealth although she has no political power over the member-countries. The goals of the Commonwealth is founded on the principles of democracy, good governance, individual liberty, free trade, world peace, human rights, and rule of law, among others. The Commonwealth functions like an international organization more than a political association with no country exercising any control over the others.
About the Author:
Teresa is a researcher-writer who covers a wide range of topics in search of useful information.
Image: ilga.org